Your shopping cart is empty.
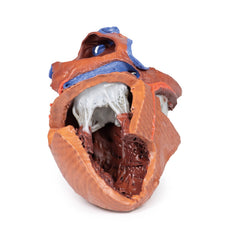
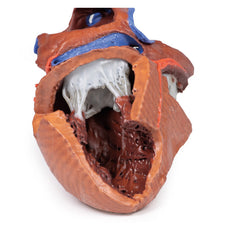
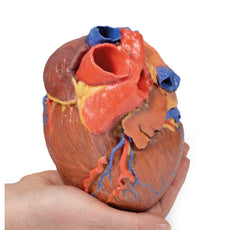
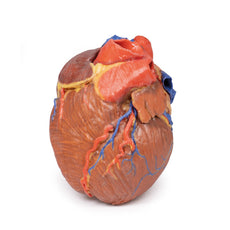
3D Printed Acute Syphilitic Aneurysm
Item # MP2042Need an estimate?
Click Add To Quote

-
by
A trusted GT partner -
FREE Shipping
U.S. Contiguous States Only -
3D Printed Model
from a real specimen -
Gov't pricing
Available upon request
3D Printed Acute Syphilitic Aneurysm
Clinical History
A 61-year old male presents with exertional anginal chest pain and dyspnoea. He
has had these
symptoms for 6 years with increasing severity. On examination, he is cyanotic and tachycardic with a collapsing
pulse. A swelling was noted on the right side of his neck. There was a thrill in his carotid artery. The apex beat
was displaced inferolaterally. A loud systolic and diastolic murmur was auscultated in the aortic area. Chest X-rays
showed cardiomegaly with a large rounded lesion in the right upper mediastinum continuous with the heart shadow with
radiographic evidence of cardiac failure. Blood tests were positive for anti-treponemal antibodies. The patient‘s
condition deteriorated and he died of cardiac failure.
Pathology
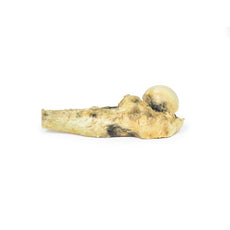
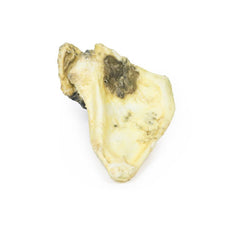
This specimen is the patient‘s enlarged heart, including the aortic arch and descending
aorta. The
ascending aorta is dilated up to 7 cm in diameter, and is expanded superiorly by a large aneurysmal bulge 11 x 13 cm
in diameter. This has been opened to display the wrinkled scarred intimal surface. There is also marked atheroma of
the intima. The innominate, left common carotid and subclavian arteries have been displaced towards the patients
left by the aneurysm. On the internal surface of the aneurysm there is a ridge-like thickening 5 mm high. This is
the site of attachment of the pericardial sac externally. There is marked congestion of small blood vessels in the
adventitia of the aorta. This is a syphilitic aneurysm of the arch of the aorta.
Further Information
Syphilis is a chronic infection caused by the spirochete Treponema pallidum.
Sexually
transmitted infection is most common but it may also be congenitally acquired by transplacental transmission of the
bacteria. Those who have the higher risk of syphilis infection include those of a sexually active age, intravenous
drug user, HIV-infected patients and male same sex relationships. Syphilis infection rates decreased significantly
with the introduction of penicillin in 1943; it remains the main treatment today. However, the infection rate has
been increasing since the early 2000s.
Syphilis is divided into three clinical stages with distinct clinical and
pathological features with characteristic proliferative endarteritis affecting small vessels.
Primary syphilis
occurs usually 3 weeks after initial infection. This manifests typically as a single, painless and erythematous
lesion called a chancre at the site of inoculation. The syphilis spreads throughout the body from this chancre which
then heals spontaneously after 3 to 6 weeks.
Secondary syphilis occurs weeks to a few months after the primary
chancre resolves in 75% of untreated patients. During this stage patients commonly have generalised symptoms, such
as malaise and lymphadenopathy and skin rashes. Palmar/plantar rashes are the most frequent site but rashes can be
diffuse. These rashes can be maculopapular, scaly or putular.
Condylomata lata are elevated gray plaques that arise on the moist mucous membranes such as oral or genital regions.
Other less common manifestations include hepatitis, gastrointestinal invasion or ulceration and neurosyphilis –
discussed below.
Tertiary syphilis has three main characteristics: cardiovascular syphilis, neurosyphilis and
gummatous syphilis. These occur after a latent period of 5 years or more in of untreated patients. Cardiovascular
syphilis involves an aortitis for which the exact pathophysiology is unclear. The vasculitis involves the ascending
thoracic aorta leading to progressive dilation of the aortic root. This can lead to aortic valve insufficiency from
dilation of the aortic valve ring. Endarteritis of the vasa vasorum leads to scarring
of the media with loss of
muscle and elastic tissue leading to the formation of aneurysms. Clinical manifestation usually happens 15-30 years
post initial infection.
Neurosyphilis can be symptomatic or asymptomatic. It occurs in 10% of untreated patients.
Early clinical manifestations include headaches, meningitis, hearing loss and ocular involvement, most commonly
uveitis, causing vision loss. Late manifestations can occur up to 25 years post initial infection. Main features are
meningovascular neurosyphilis, paretic neurosyphilis and tabes dorsalis. Meningovascular involvement involves
chronic meningitis and endarteritis which can lead to strokes. Tabes dorsalis is caused from degeneration of the
posterior columns within the spinal cord. This causes loss of proprioception, ataxia, loss of pain sensation, and
loss of reflexes. Paretic neurosyphilis is caused by invasion and damage of the brain parenchyma, most commonly the
frontal lobes. This leads to progressive cognitive impairment and mood disturbance.
Gummatous syphilis is
characterised by the formation of nodular lesions most commonly bone, skin and mucosa of the upper airway and mouth
called gummas. These can occur anywhere including viscera. The formation of gummas is rare but occurs more
frequently in HIV-infected patients. Skeletal involvement causes pain and pathological fractures.
 Handling Guidelines for 3D Printed Models
Handling Guidelines for 3D Printed Models
GTSimulators by Global Technologies
Erler Zimmer Authorized Dealer
The models are very detailed and delicate. With normal production machines you cannot realize such details like shown in these models.
The printer used is a color-plastic printer. This is the most suitable printer for these models.
The plastic material is already the best and most suitable material for these prints. (The other option would be a kind of gypsum, but this is way more fragile. You even cannot get them out of the printer without breaking them).The huge advantage of the prints is that they are very realistic as the data is coming from real human specimen. Nothing is shaped or stylized.
The users have to handle these prints with utmost care. They are not made for touching or bending any thin nerves, arteries, vessels etc. The 3D printed models should sit on a table and just rotated at the table.