Your shopping cart is empty.
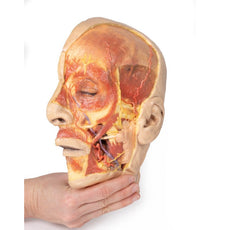
3D Printed Endometrial Carcinoma
Item # MP2106Need an estimate?
Click Add To Quote

-
by
A trusted GT partner -
FREE Shipping
U.S. Contiguous States Only -
3D Printed Model
from a real specimen -
Gov't pricing
Available upon request
3D Printed Endometrial Carcinoma
Clinical History
A 63-year old woman presented with a history of dull lower abdominal pain for 2
months and heavy persistent vaginal bleeding for 1 week. The menopause had occurred 13 years previously. Radical
abdominal hysterectomy and bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy were commonly performed for the treatment of endometrial
cancer following confirmation of endometrial carcinoma in biopsy.
Pathology
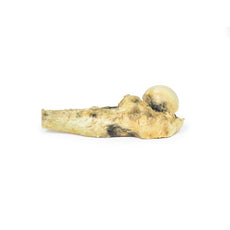
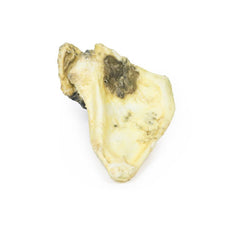
The specimen consists of uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries. The endometrial cavity
and endocervical canal have been opened on the anterior aspect. The endometrial lining is grossly abnormal
especially on the right side and a brown polypoid tumour has invaded the myometrium and extends inferiorly into the
cervical canal. Histologically this was a well-differentiated adenocarcinoma of the endometrium. The left ovary,
which has been sectioned in the coronal plane, is enlarged and has several large follicular cysts/cavities.
Further Information
Endometrial carcinoma is the most common gynecological malignancy in
developed countries and the second most common in developing countries after cervical cancer. There are two major
types of endometrial carcinoma. Endometroid carcinoma account for almost 80% of endometrial carcinoma. They usually
present early and so have a more favourable outcome. These tumours may arise from atypical endometrial hyperplasia.
Common genetic abnormalities seen in endometrioid tumours are mutations in the PTEN, PIK3Ca and ARID1A genes. Serous
carcinoma are a less common form of endometrial carcinoma. These tumours are associated with mutations in TP53 gene
and carry a poorer prognosis. Endometrioid tumours tend to affect women aged 55 to 65 years. Risk factors for
developing endometrioid endometrial cancer include obesity, impaired glucose tolerance, infertility, unopposed
estrogen therapy (e.g. early menarche, late menopause or exogenous sources). Serous neoplasms affect older women
aged 65 to 75 years with other risk factors for development include having a lower BMI and an atrophic uterus. Women
with Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colorectal Cancer (Lynch Syndrome) have a significantly higher risk of developing
endometrial cancer.
The most common symptom of endometrial cancer is abnormal vaginal bleeding. Most frequently it presents as post-menopausal bleeding, which often allows early presentation. Others may be asymptomatic or an incidental finding of an abnormal endometrium on abdominopelvic imaging. The main radiological sign of endometrial cancer is abnormally thickened endometrium on pelvic ultrasound or CT scan. Diagnosis is made on endometrial biopsy, endometrial curettage or hysterectomy. Treatment depends on the stage of the cancer and includes local radiotherapy, systemic chemotherapy and surgical hysterectomy +/- salpingo-oophorectomy.
Download: Handling Guidelines for 3D Printed Models
Handling Guidelines for 3D Printed Models
GTSimulators by Global Technologies
Erler Zimmer Authorized Dealer
The models are very detailed and delicate. With normal production machines you cannot realize such details like shown in these models.
The printer used is a color-plastic printer. This is the most suitable printer for these models.
The plastic material is already the best and most suitable material for these prints. (The other option would be a kind of gypsum, but this is way more fragile. You even cannot get them out of the printer without breaking them).The huge advantage of the prints is that they are very realistic as the data is coming from real human specimen. Nothing is shaped or stylized.
The users have to handle these prints with utmost care. They are not made for touching or bending any thin nerves, arteries, vessels etc. The 3D printed models should sit on a table and just rotated at the table.