Your shopping cart is empty.
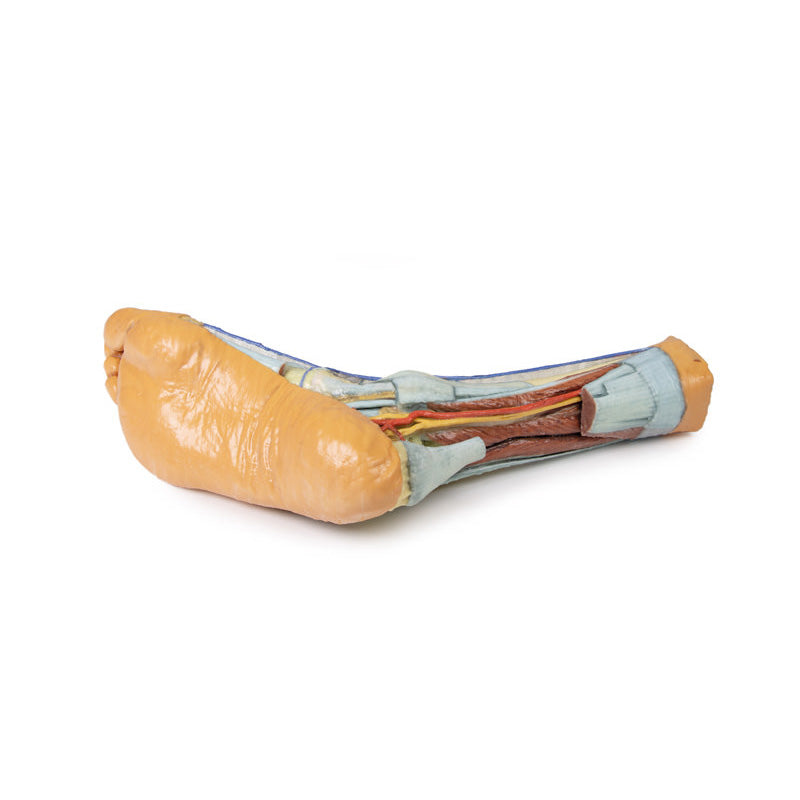
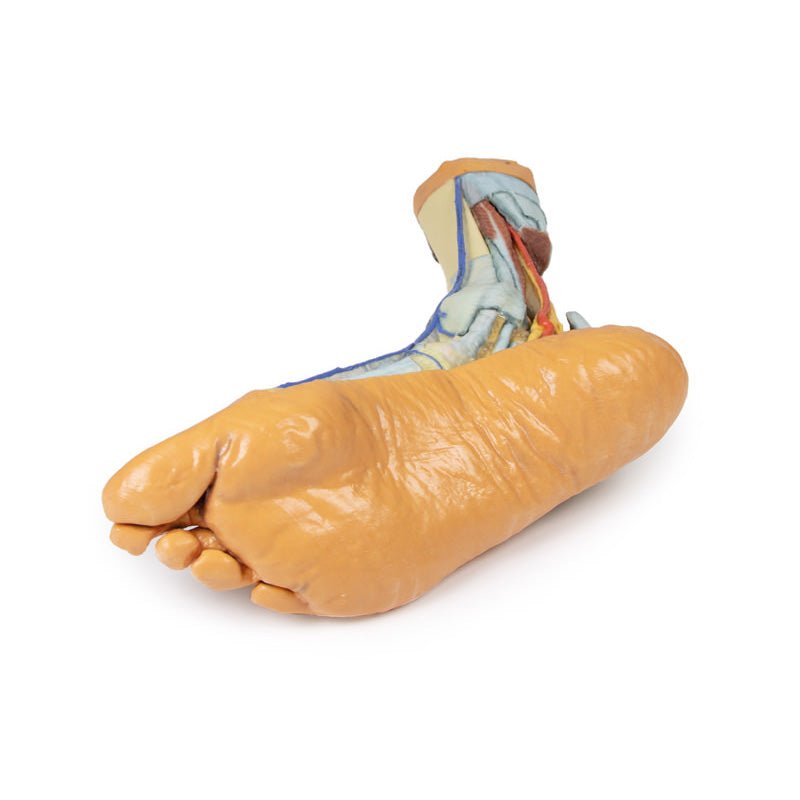
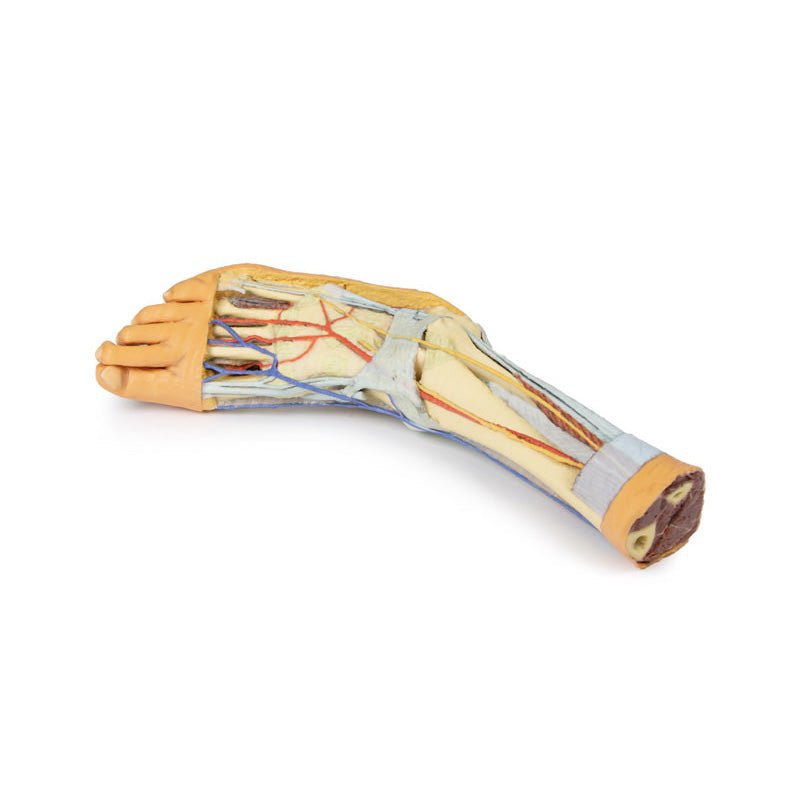
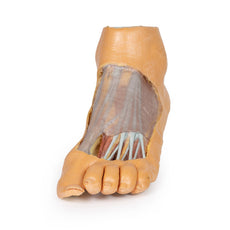
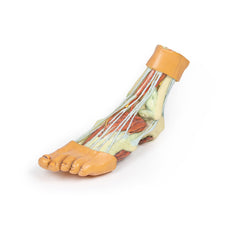
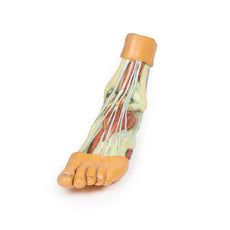
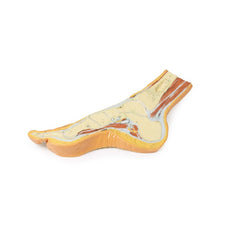
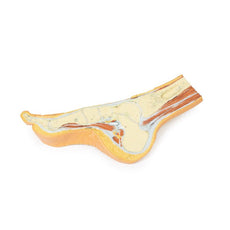
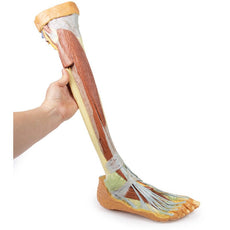
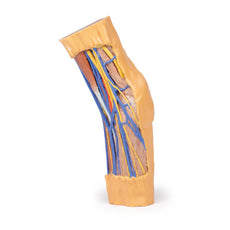
3D Printed Foot with deep structures of the distal leg and foot
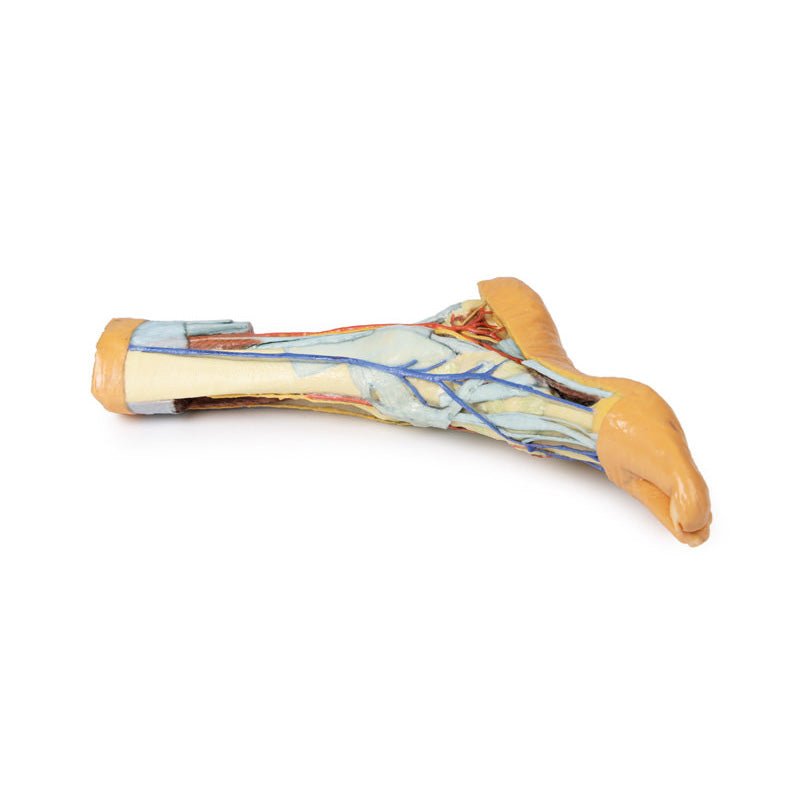
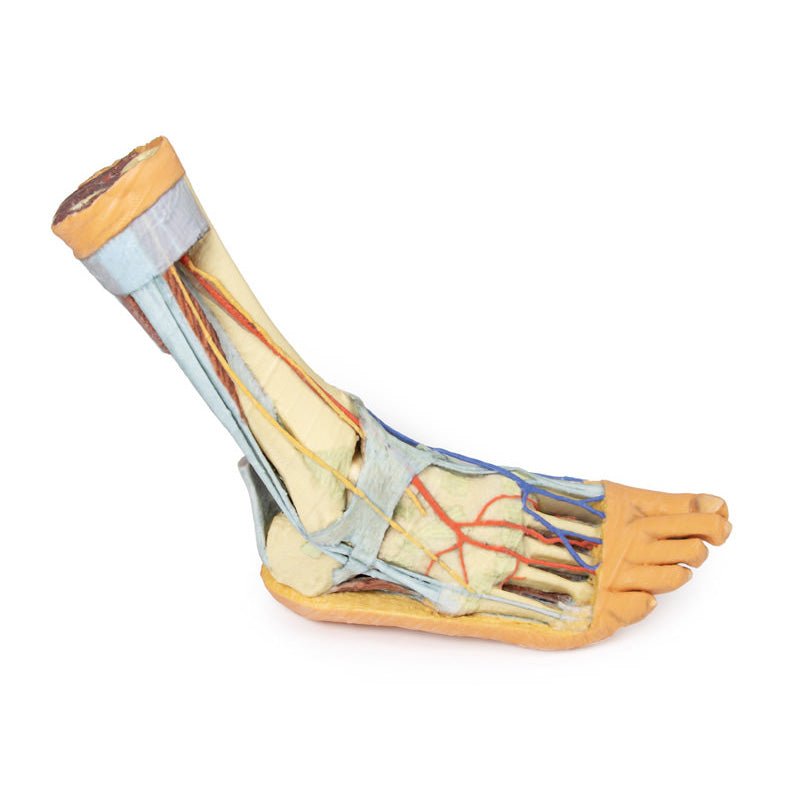
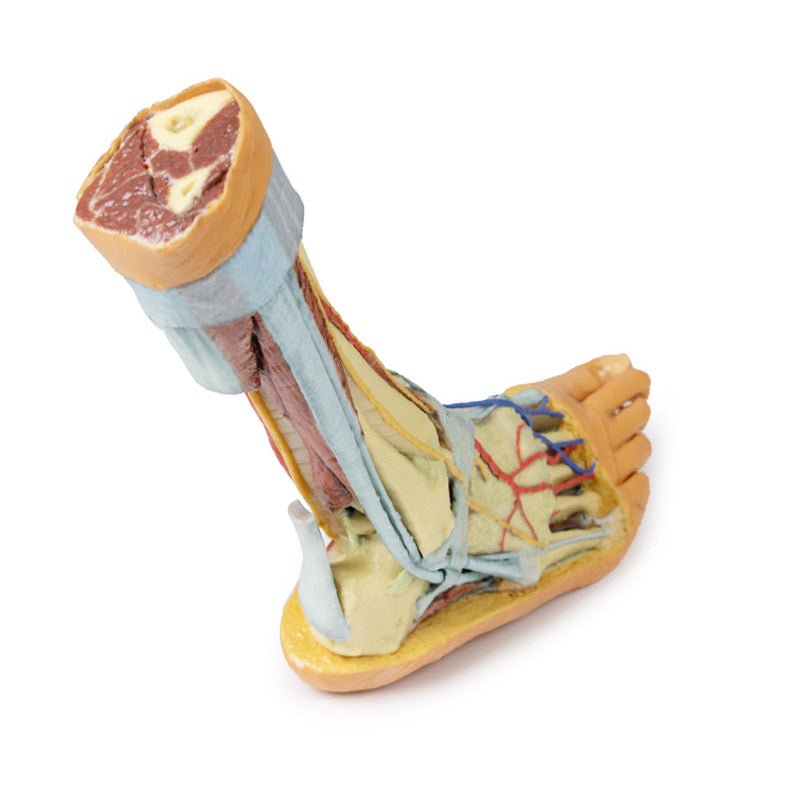
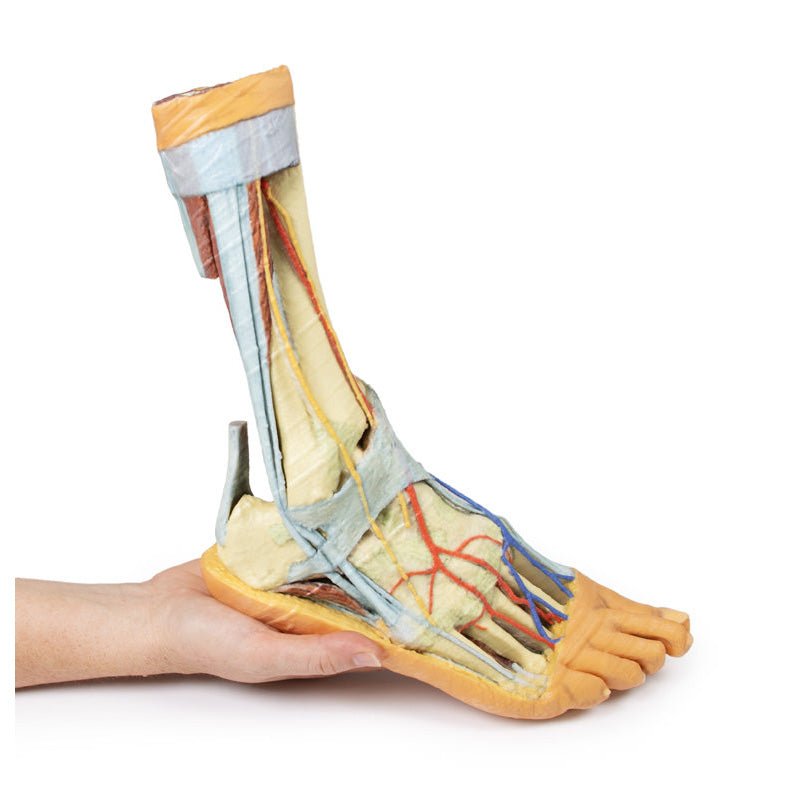
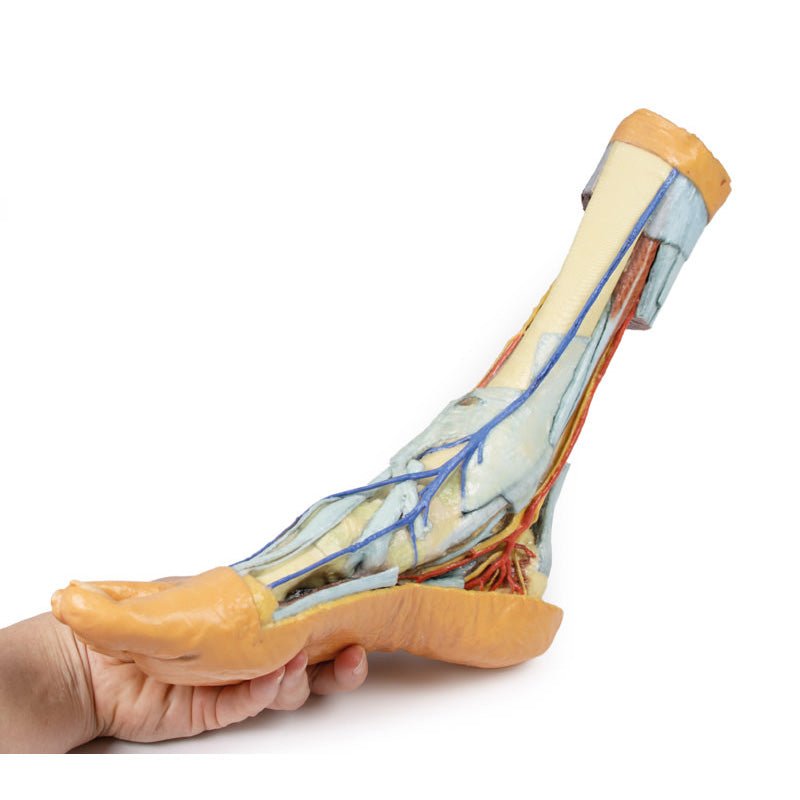
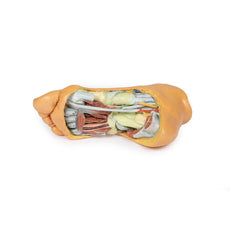
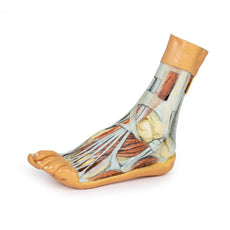
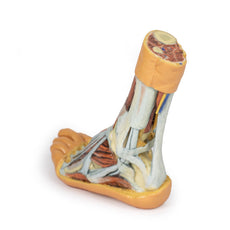
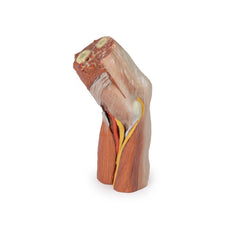
Adjacent to these muscles the course of the tibial nerve and posterior tibial artery can be followed to the origin of the medial and lateral plantar branches at the level of the flexor retinaculum. The origin of the abductor hallucis brevis muscle has been removed to expose more of the artery and nerve branches.
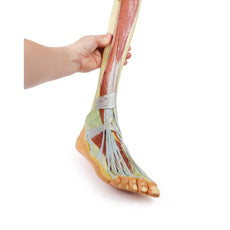
The origin of the great saphenous vein from the medial aspect of the dorsal venous arch is preserved, with the vessel ascending to the cut edge of the specimen. Although the anterior compartment muscles have been removed to demonstrate the interosseous membrane, the course of the anterior tibial artery, and the deep fibular nerve to the dorsum of the foot; the tendinous insertions of the tibialis anterior, extensor hallucis longus, and the hallucal tendon of the extensor digitorum longus have been retained passing deep to the inferior extensor retinaculum.
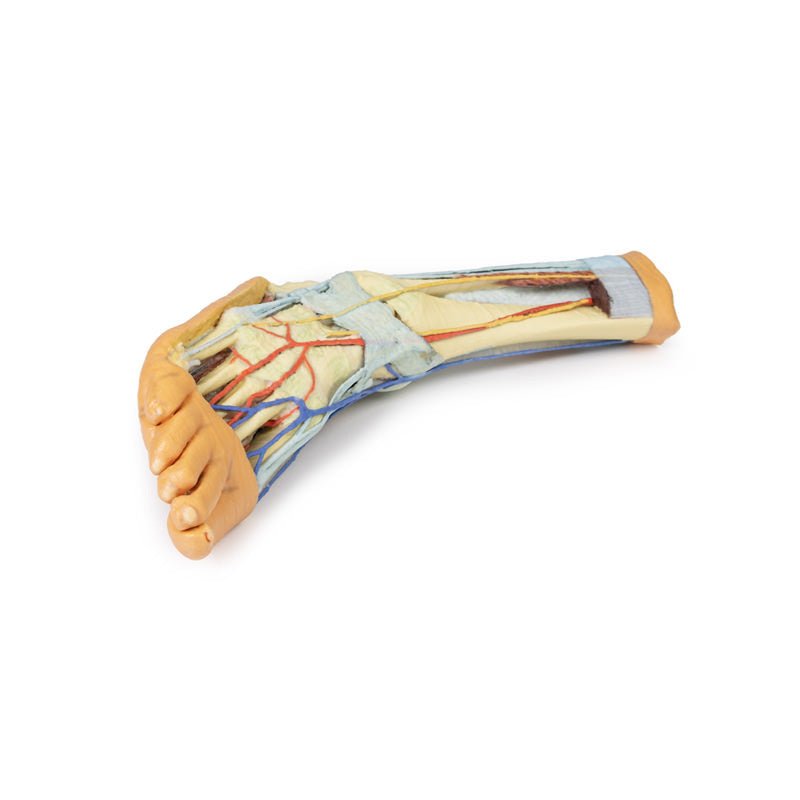
The anterior tibial artery is continuous through dorsalis pedis to the arcuate artery and the dorsal metatarsal arteries. The removal of the dorsal interosseous muscles demonstrate the approach of these terminal branches to the plantar interosseous muscles.
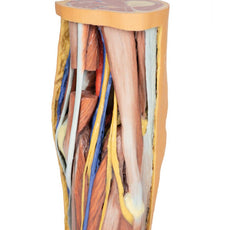
On the lateral aspect of the specimen, the fibularis longus and fibularis brevis muscles and tendons are visible, with tendons passing deep to the cut edge of the superior fibular retinaculum and complete inferior fibular retinaculum.
Adjacent to the insertion of the fibularis brevis is the preserved tendon of the extensor digitorum longus to the fifth digit and the termination of the superficial fibular nerve; adjacent to the fibularis longus tendon entering the plantar surface of the foot is the origin of the abductor digiti minimi muscle.
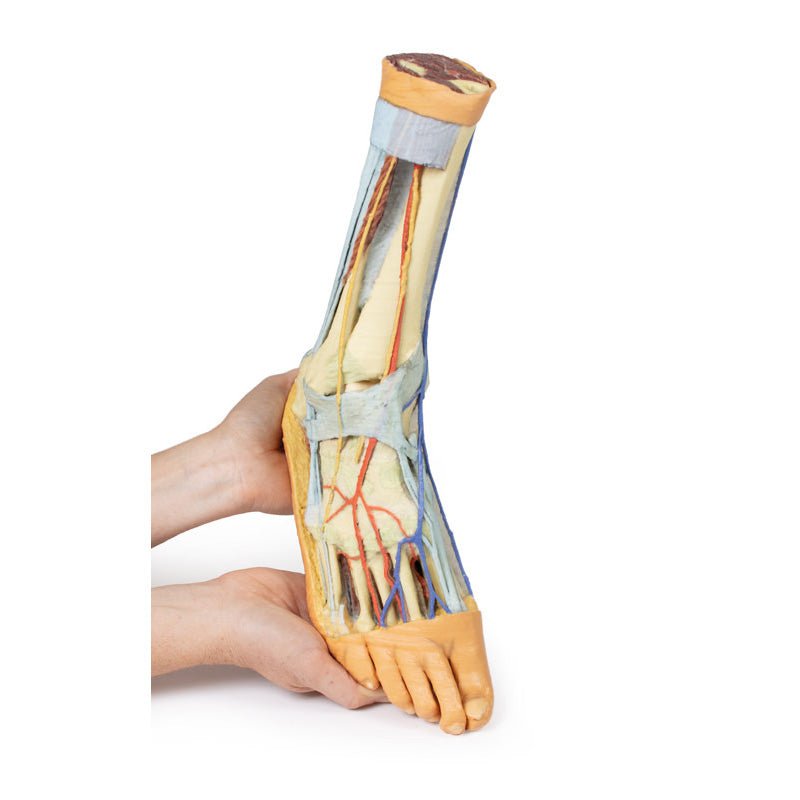
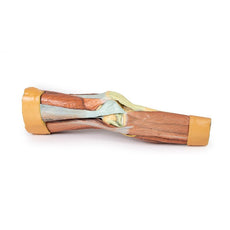
Deep to these more superficial structures are several of the distal leg and foot ligaments, including the anterior and posterior tibiofibular ligaments, calcaneofibular ligament, dorsal and posterior talonavicular ligaments, and the deltoid ligament.
Download:
GTSimulators by Global Technologies
Erler Zimmer Authorized Dealer

9.0 lb
🎄 HOLIDAY SAVINGS - Ends Dec 31 🎄
Discount has been automatically applied for this item.
3D Printed Foot with deep structures of the distal leg and foot
Item # MP1930
$1,880.00
$2,089.00
You save $209.00
Need an estimate?
Click Add To Quote

Features & Specifications
-
by
A trusted GT partner -
3D Printed Model
from a real specimen -
Gov't pricing
Available upon request
Frequently Bought Together
3D Printed Foot - Superficial and deep structures of the distal leg and foot
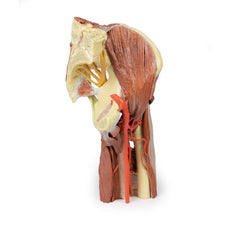
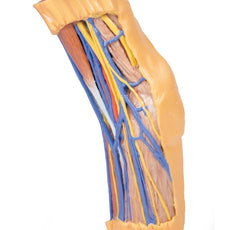
This 3D printed specimen presents both superficial and deep structures of a right distal leg and foot. Proximally, the posterior compartment of the leg has been dissected to remove the triceps surae muscles and tendocalcaneous to demonstrate the deep muscles of the compartment (tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum longus, flexor hallucis longus).Adjacent to these muscles the course of the tibial nerve and posterior tibial artery can be followed to the origin of the medial and lateral plantar branches at the level of the flexor retinaculum. The origin of the abductor hallucis brevis muscle has been removed to expose more of the artery and nerve branches.
The origin of the great saphenous vein from the medial aspect of the dorsal venous arch is preserved, with the vessel ascending to the cut edge of the specimen. Although the anterior compartment muscles have been removed to demonstrate the interosseous membrane, the course of the anterior tibial artery, and the deep fibular nerve to the dorsum of the foot; the tendinous insertions of the tibialis anterior, extensor hallucis longus, and the hallucal tendon of the extensor digitorum longus have been retained passing deep to the inferior extensor retinaculum.
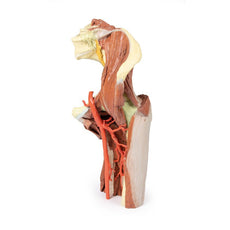
The anterior tibial artery is continuous through dorsalis pedis to the arcuate artery and the dorsal metatarsal arteries. The removal of the dorsal interosseous muscles demonstrate the approach of these terminal branches to the plantar interosseous muscles.
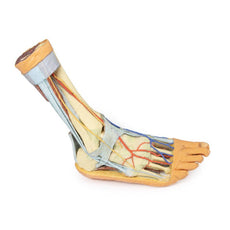
On the lateral aspect of the specimen, the fibularis longus and fibularis brevis muscles and tendons are visible, with tendons passing deep to the cut edge of the superior fibular retinaculum and complete inferior fibular retinaculum.
Adjacent to the insertion of the fibularis brevis is the preserved tendon of the extensor digitorum longus to the fifth digit and the termination of the superficial fibular nerve; adjacent to the fibularis longus tendon entering the plantar surface of the foot is the origin of the abductor digiti minimi muscle.
Deep to these more superficial structures are several of the distal leg and foot ligaments, including the anterior and posterior tibiofibular ligaments, calcaneofibular ligament, dorsal and posterior talonavicular ligaments, and the deltoid ligament.
Download:
GTSimulators by Global Technologies
Erler Zimmer Authorized Dealer
These items normal warranty are two years, however the warranty doesn’t cover “wear and tear”. The manufacturer does have 100% quality control on these models.
The models are very detailed and delicate. With normal production machines you cannot realize such details like shown in these models.
The printer used is a color-plastic printer. This is the most suitable printer for these models.
The plastic material is already the best and most suitable material for these prints. (The other option would be a kind of gypsum, but this is way more fragile. You even cannot get them out of the printer without breaking them).The huge advantage of the prints is that they are very realistic as the data is coming from real human specimen. Nothing is shaped or stylized.
The users have to handle these prints with utmost care. They are not made for touching or bending any thin nerves, arteries, vessels etc. The 3D printed models should sit on a table and just rotated at the table.
The models are very detailed and delicate. With normal production machines you cannot realize such details like shown in these models.
The printer used is a color-plastic printer. This is the most suitable printer for these models.
The plastic material is already the best and most suitable material for these prints. (The other option would be a kind of gypsum, but this is way more fragile. You even cannot get them out of the printer without breaking them).The huge advantage of the prints is that they are very realistic as the data is coming from real human specimen. Nothing is shaped or stylized.
The users have to handle these prints with utmost care. They are not made for touching or bending any thin nerves, arteries, vessels etc. The 3D printed models should sit on a table and just rotated at the table.

by — Item # MP1930
3D Printed Foot with deep structures of the distal leg and foot
$1,880.00
$2,089.00
Add to Cart
Add to Quote